-
Partager cette page
Testing the Effect of Relative Pollen Productivity on the REVEALS Model: A Validated Reconstruction of Europe-Wide Holocene Vegetation
Publication du premier article de Maria Antonia SERGE dans la revue Land. Cette étude présente les reconstructions palynologiques les plus étendues spatialement et continuellement temporelles de la couverture végétale en Europe sur l'ensemble de l'Holocène. Ces reconstructions quantitatives fiables de la végétation sont essentielles pour améliorer notre compréhension de la dynamique des paysages. Elles nous permettent d'évaluer les effets passés des variables environnementales et des changements d'utilisation des terres sur les écosystèmes et la biodiversité, et de mieux atténuer leurs effets à l'avenir.
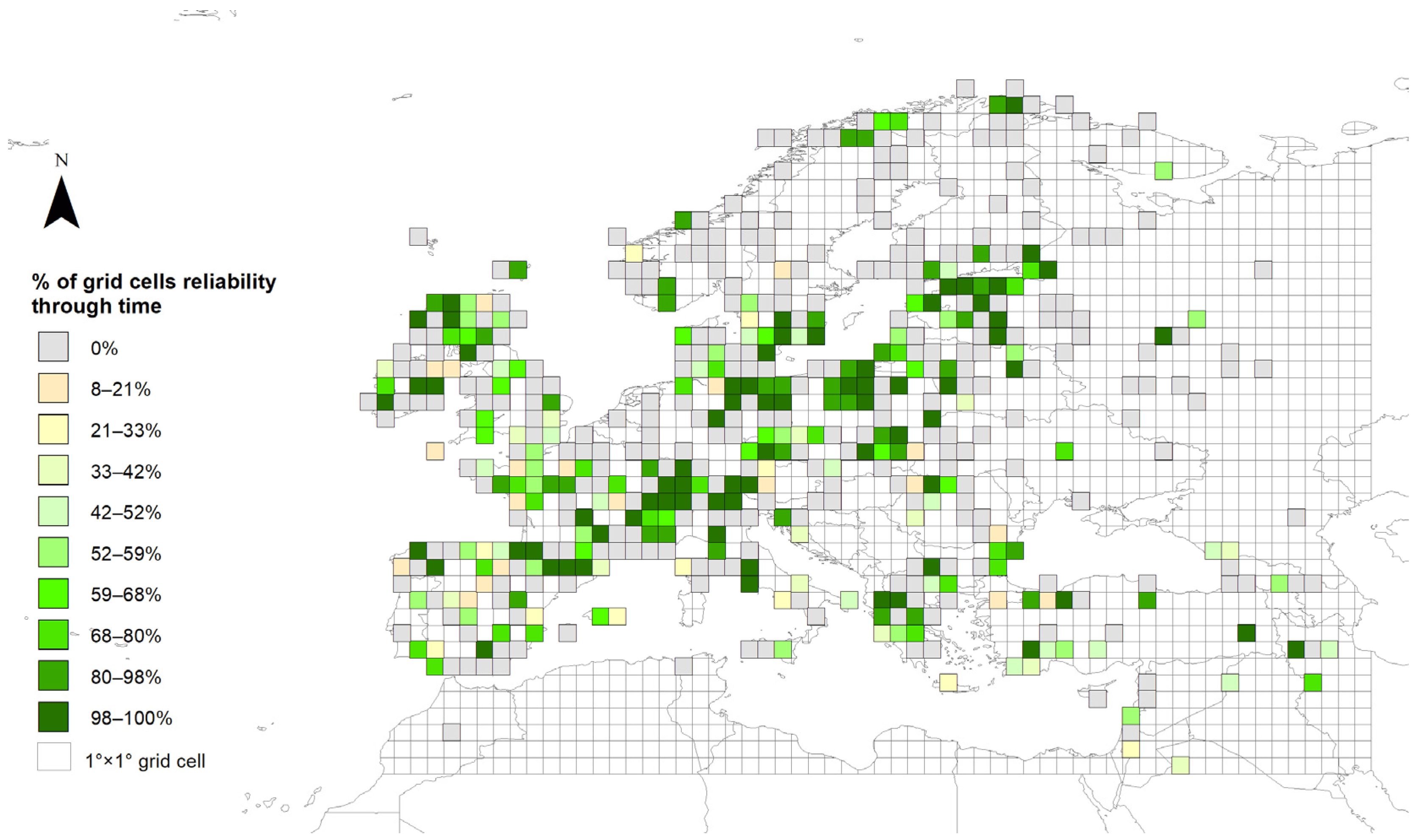
We present here the most spatially extensive and temporally continuous pollen-based reconstructions of plant cover in Europe (at a spatial resolution of 1° × 1°) over the Holocene (last 11.7 ka BP) using the ‘Regional Estimates of VEgetation Abundance from Large Sites’ (REVEALS) model. This study has three main aims.
- First, to present the most accurate and reliable generation of REVEALS reconstructions across Europe so far. This has been achieved by including a larger number of pollen records compared to former analyses, in particular from the Mediterranean area.
- Second, to discuss methodological issues in the quantification of past land cover by using alternative datasets of relative pollen productivities (RPPs), one of the key input parameters of REVEALS, to test model sensitivity.
- Finally, to validate our reconstructions with the global forest change dataset. The results suggest that the RPPs.st1 (31 taxa) dataset is best suited to producing regional vegetation cover estimates for Europe. These reconstructions offer a long-term perspective providing unique possibilities to explore spatial-temporal changes in past land cover and biodiversity.
Lire la suite de l'article sur LAND




